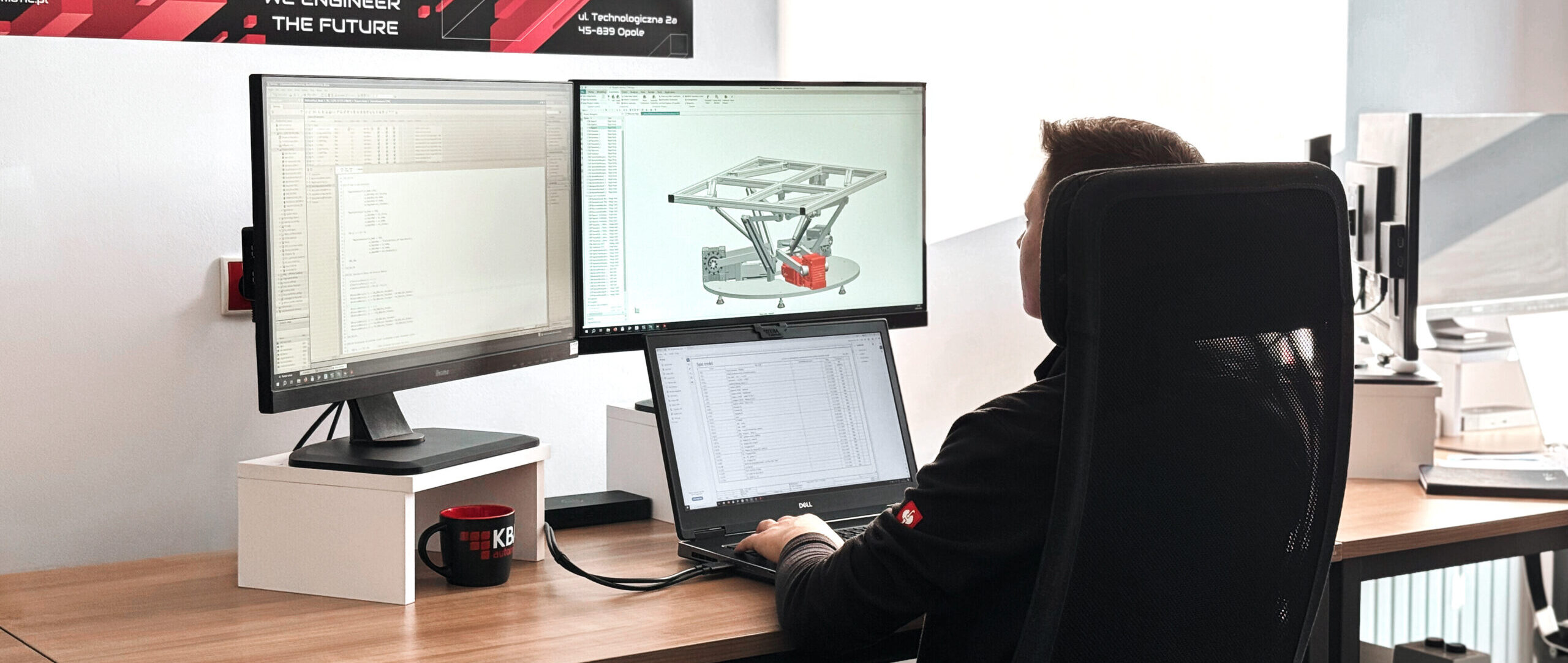


Nowadays, in industry we can encounter highly automated systems. Those include various types of conveyors, robots, safety equipment, and many other industrial machines that, despite such variety, are controlled by one specific device – a PLC.
Conventional approach to commissioning automated industrial lines consists of two stages: offline PLC program preparation, and direct testing and commissioning at the facility, known as onsite commissioning. Although it often turns out that the created control algorithm hides flaws and deficiencies, which causes a delay in the whole process.
To prevent this additional step, virtual commissioning is performed before implementation of the developed solution at the facility.
Virtual commissioning is a modern approach to the development and implementation of automated systems that allows lines and machines to be simulated, tested and optimized using a virtual environment before physical onsite application. This process perfectly fills the gap between design, commissioning and deployment phases, resulting in time savings, cost reductions, as well as minimized risks during commissionig.
The virtual commissioning process begins with the creation of a 3D model of the system in a specialized simulation software. This model is then integrated with a PLC and optionally an HMI, where the actual code is run. This allows all scenarios and procedures to be tested as if they have occurred in a real facility. The most important benefit of virtual commissioning is that the PLC code can be debugged in the simulation environment, allowing the software to be optimized before being transferred to the physical system.
In addition, by simulating and validating automation solutions through the virtual commissioning process, it is possible to confirm that they will work as expected on site, which significantly reduces commissioning time.
Let’s take a detailed look at the benefits of the virtual commissioning process:
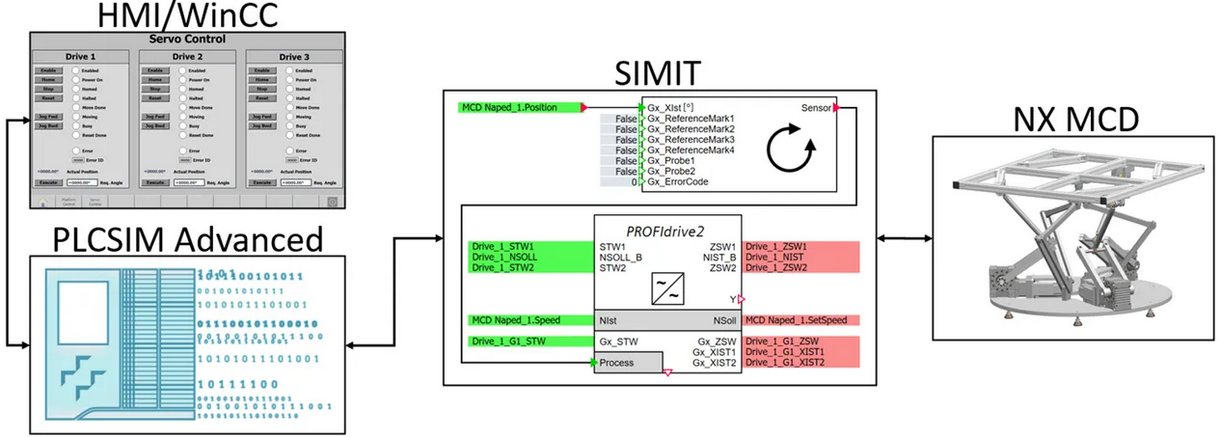
Siemens NX MCD is a tool used to design and simulate mechatronic systems. During the virtual commissioning process, NX MCD allows the creation of detailed 3D models of machines and systems. It integrates mechanical, electrical and software components into one model. As a result, we obtain a model which simulates the physical behavior and interactions of individual components with each other. The software allows for the simulation of kinematics, dynamics and control logic, which helps us understand how the system will behave in real-world conditions. NX MCD is most often used as a basis for developing and refining the mechanical design before moving on to more advanced simulations. Further, with additional PLC simulation software (such as PLC-Sim Advanced), it is possible to verify the correct operation of the prepared code for the PLC.
SIMIT is a simulation tool used to create a virtual replica (digital twin) of an automation system. At the virtual commissioning stage, SIMIT enables the integration of virtual 3D models from NX MCD with a real PLC code. This platform emulates the real-time behavior of the control system, including input/output signals, sensors and actuators. By using this software, it is possible to test and verify the control logic while ensuring that the PLC code will work correctly when implemented on the physical hardware. Simulation using SIMIT software helps detect errors and optimize control logic, reducing the risk of failure during the field commissioning phase.
Tecnomatix Plant Simulation is used to simulate and optimize the performance of manufacturing systems and logistics operations. In the context of virtual commissioning, Plant Simulation is a detailed simulation environment for analyzing material flow, production rates and potential bottlenecks in a system. With this software, it is possible to improve the layout, sequence, and operation of machines to ensure an efficient and effective production. Plant Simulation also identifies potential capacity and resource utilization issues that can be resolved before the actual implementation, leading to smoother operations and reduced downtime.
Tecnomatix Process Simulate is a tool meant for simulating and validating manufacturing processes. It allows to reproduce manufacturing processes, assembly operations and material handling in detail, also in terms of human and/or robot interactions, material handling and assembly operations. The tool can verify the feasibility of processes, optimize cycle times and ensure that safety standards are met. One of the biggest advantages of the software is its integration with other Siemens tools enabling comprehensive validation of the entire production process in a virtual environment.
Xcelgo Experior is a simulation and emulation platform that integrates with real PLCs and other control systems. In the virtual commissioning process, Experior helps to close the gap between virtual models and physical control systems. It enables real-time testing of control logic in a virtual environment, providing highly accurate simulation of the real system’s behavior. Experior supports hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing, allowing the control system to be tested with real hardware components connected to the virtual environment. As a result, hardware integration issues can be identified and resolved before implementation at the facility.
Following current trends in the industry, we can see several possible directions for the development of virtual commissioning, among others we can specify:
At our business, we use virtual commissioning in two ways. In the execution of external orders, to carry out the virtual commissioning itself, and – much more often – during the planning, programming or optimization phase of the system we are preparing.
We implemented virtual commissioning in our first R&D project for a high-precision elevator – a Stewart Platform model.
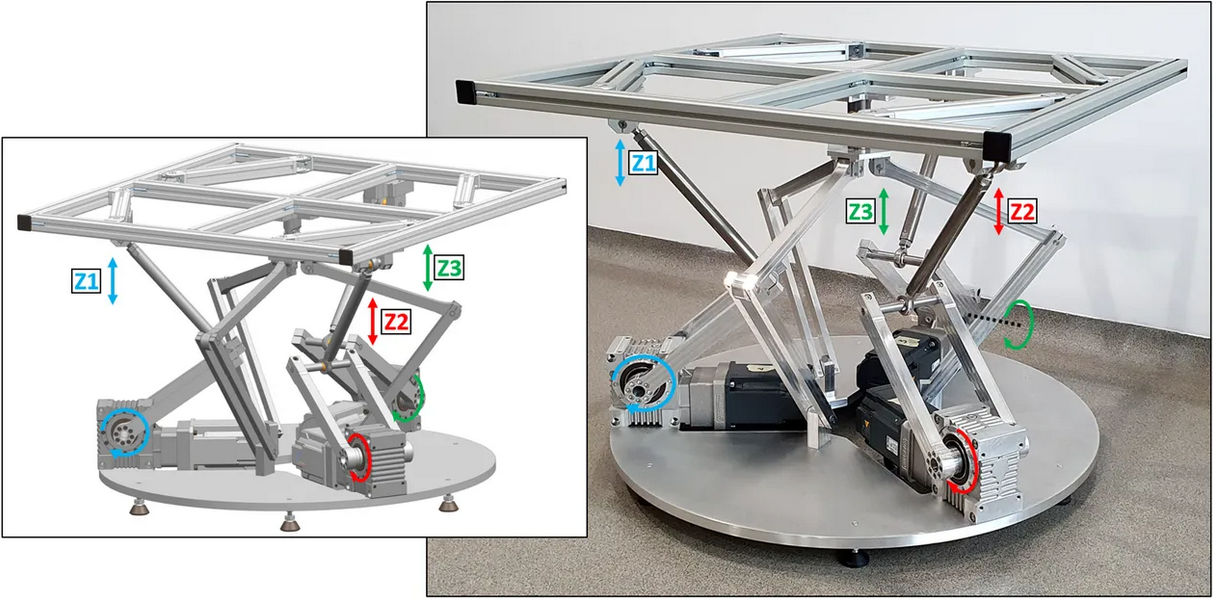
In the initial stage, we used a CAD model of the workstation we had prepared, which we imported into the Siemens NX MCD environment. This allowed us to add physics parameters, connectors and sensors to the model. Further, using the Siemens SIMIT environment has allowed us implement S210 drives using technological objects. This way, we obtained a fully mapped mechanical system.
A prepared virtual model allowed us to verify the created concept, make improvements and remove errors found in the design of the mechanical structure, as well as the PLC code. Most importantly, we were able to do this before we even started building the physical model of the system.
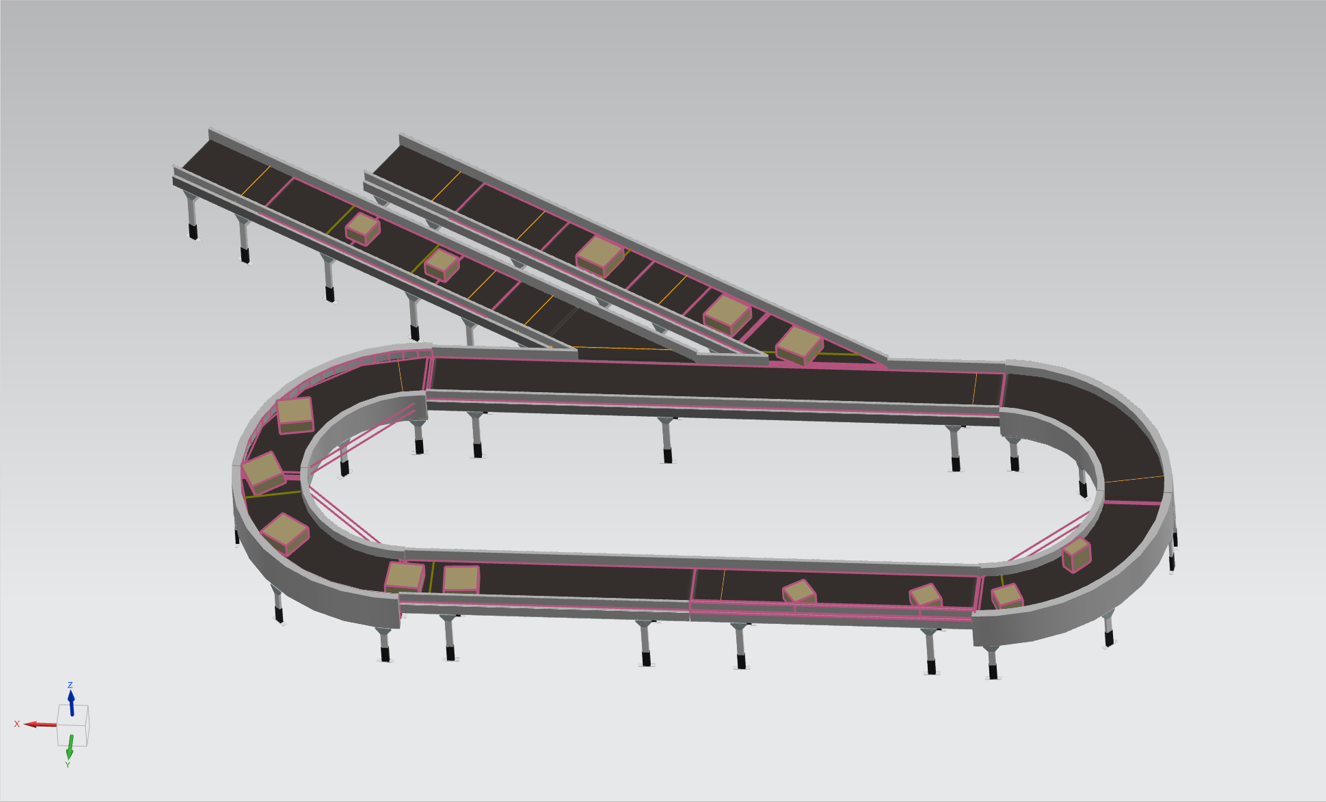
Currently, a significant part of our projects are conducted in the logistics industry. This industry is characterized by a high flow of goods through facilities, and continuous development. Because of this, it is crucial to constantly streamline and improve systems. Thus, we design new solutions and carry out their virtual commissioning using various environments, such as Siemens NX MCD and Xcelgo Experior.
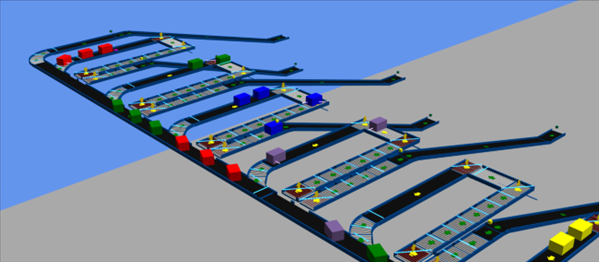
We are also implementing an R&D project to develop an intelligent transportation system for the logistics industry. In this process, we are using Siemens NX MCD software, which has already allowed us to verify our plans and assumptions for the mechanical part of the project during the initial stages, and to make corrections before physically preparing the transportation system. In addition, we use the software to conduct tests of control algorithm for the PLC. The most important aspect is that we are able to run these tests at an earlier stage, which would not be possible if the project was run in a traditional way – skipping the virtual commissioning process.
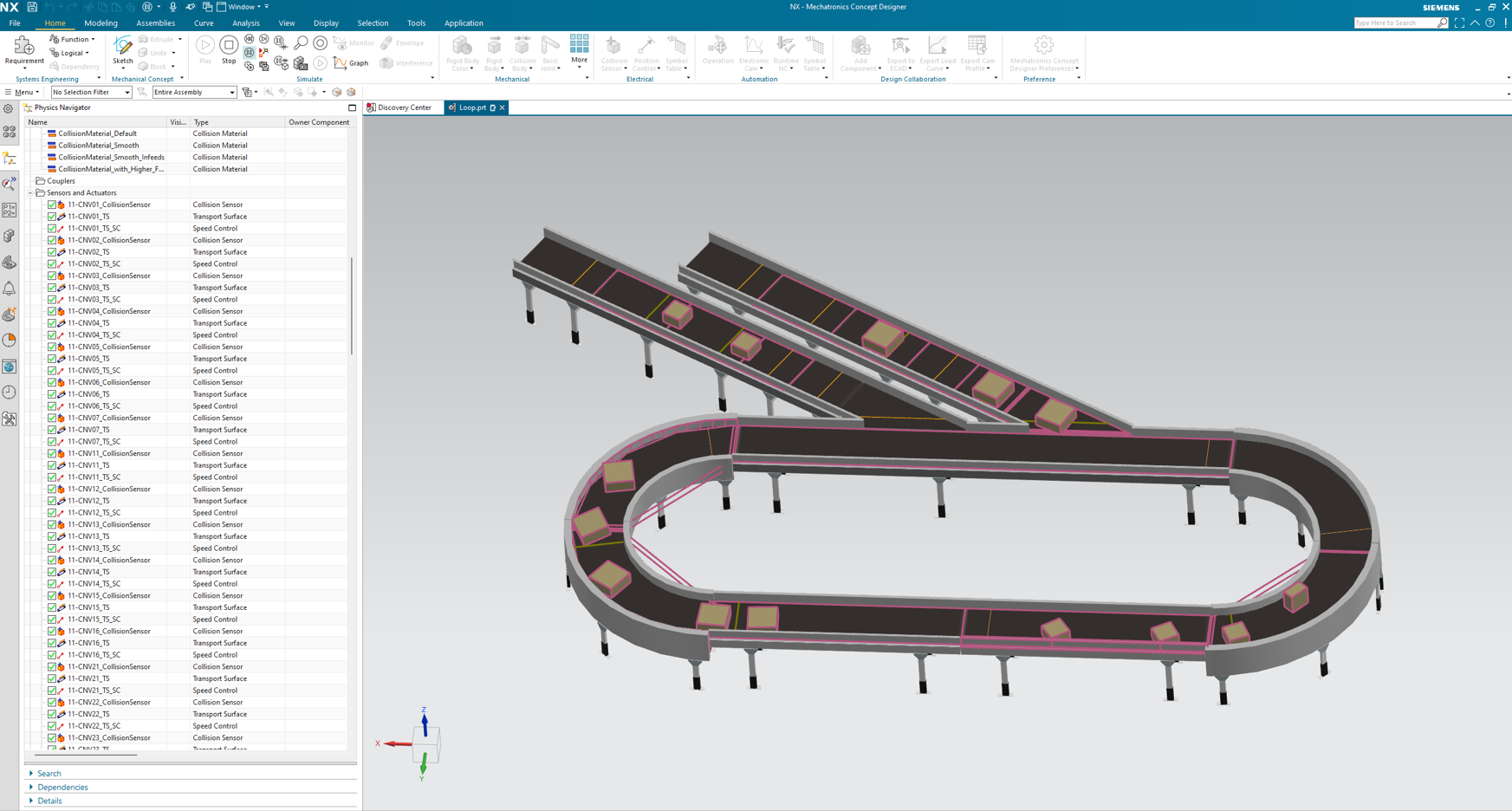
The use of simulation environments allows us to develop new control methods, or improve currently existing ones, exploring many more possible test scenarios at any given time. Moreover, the use of virtual commissioning allows us to develop system improvements more comfortably – in an office setting. And let’s not forget the reduced commissioning costs thanks to precise simulations and tests, which give us the ability to detect and fix any errors in advance.
In conclusion, virtual commissioning represents a paradigm shift in the development of automated systems, offering a robust method for simulating, testing and optimizing systems before physical deployment begins. By using advanced simulation tools and creating detailed digital twins, companies can reduce costs, improve the quality of their services and implement their products to the market faster. As technology continues to evolve, virtual commissioning will play an increasingly important role in the design and implementation of complex systems in many industries.